Introduce
PLA polymers, usually abbreviated from Poly Lactic-acids, are biodegradable polyesters synthesized from lactic acid (short as LA) or 2-hydroxy propionic acid, which can usually be obtained by bacterial fermentation of carbohydrates from agricultural plants like cassava, potatoes and corns. It is the first polymer based on renewable raw materials commercialized at a large scale. About decades ago, the use of PLA film in packaging applications was very few because of its high prices. Along with the discoveries of new pathways of polymerization and advances in manufacturing technologies, the cost of PLA polymer has been dropping dramatically, which can be commercialized as the compostable packages for more and more products, like dried fruits, snacks, coffee beans, biscuits, tea, conditments, as the list is still extending.
PBAT (short for Polybutylene Adipate Terephthalate), is a bio-degradable copolymer, specifically a copolyester with random structure of adipic acid, 1,4-butanediol and terephthalic acid. It is usually made from renewable resources such as sugar cane and corn starch, which enables it finding more applications in packaging area and consumer goods, as consumers and businesses look for more sustainable solutions. The flexibility and toughness of PBAT makes it ideal for blending with another biodegradable polymer that is strong and rigid for biodegradable film production.
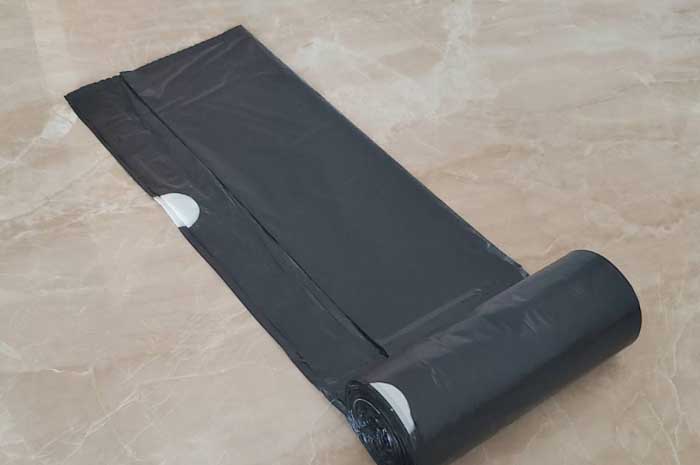
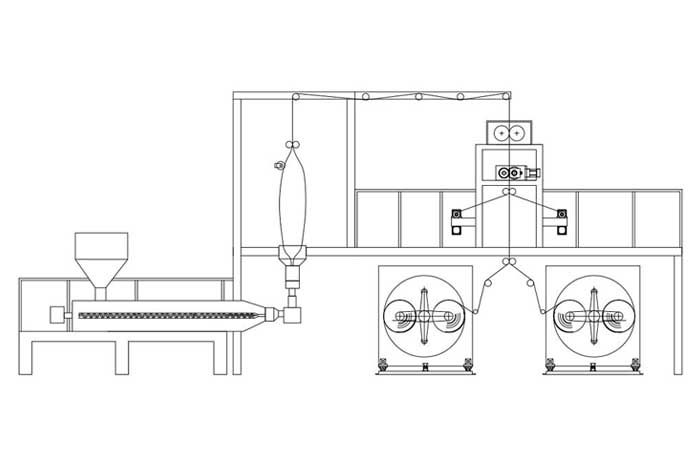
As to the PLA+PBAT film we adapt in our converting business, the film is actally a blend of PLA and PBAT polymer, with specific additives and plasticizer, to achieve the expected properties in the commercial market.
So, we name it PLA+PBAT Film.